8 Important Developments in Cybersecurity (2023) - Course Monster Blog Cybersecurity

The field of cybersecurity is always in a state of flux, with continuous changes occurring.
Although the field of data protection is not novel anymore, new enterprises, software, and devices are necessitating novel degrees of security, sometimes even calling for entirely new strategies.
Outline below the current and future noteworthy cybersecurity trends.
1. IoT Creates New Cybersecurity Threats
The significant surge in cyberattacks observed in the past decade can be attributed to the substantial proliferation of new technologies and devices.
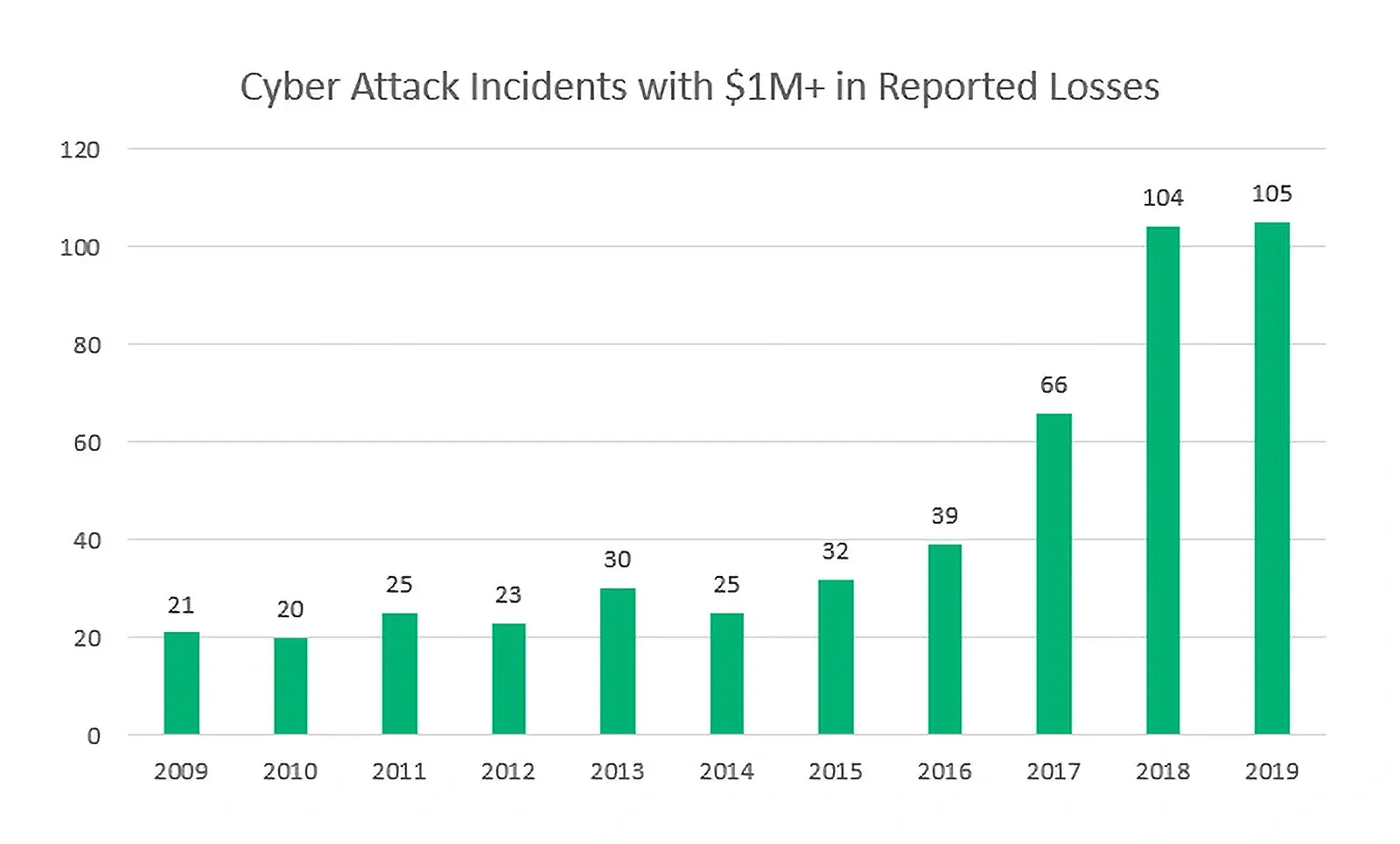
Source: Infosec Insights
The term “Internet of Things” (IoT) pertains to the vast number of physical devices worldwide that collect and exchange data over the internet. According to IDC, a global technology research firm, the number of connected IoT devices is expected to exceed 41 billion by 2025.
As the number of devices continues to proliferate, the risk of cyberattacks is growing at an exponential pace, making it challenging for security firms to keep up with the increasing demand for protection.
As per a report published by F-Secure, the tally of cyberattacks documented during the first half of 2019 surged by twelvefold in comparison to the previous year. This remarkable increase is attributed to the widespread adoption of IoT devices.
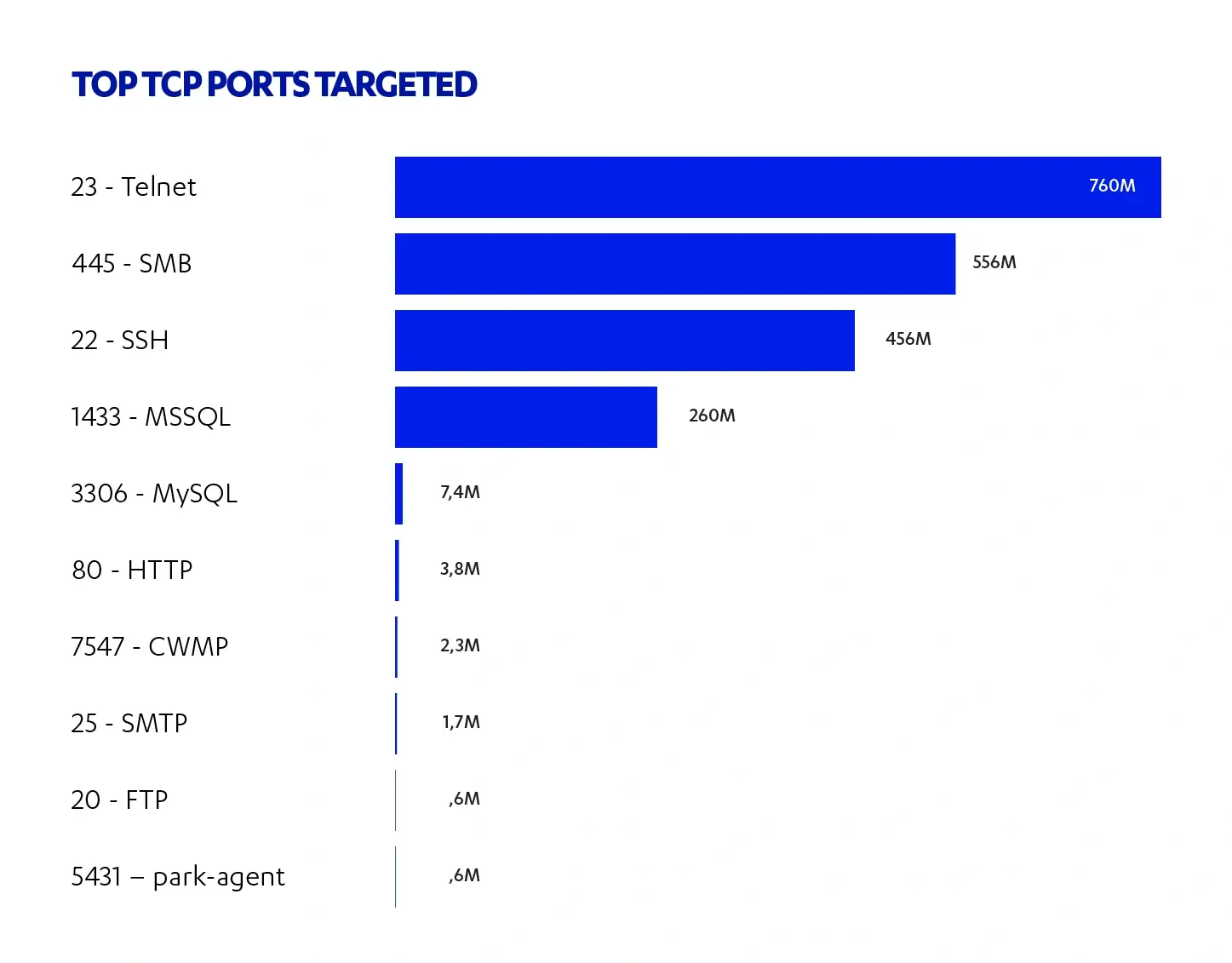
Source: F-Secure
From fitness watches to baby monitors, every device is vulnerable to security breaches, prompting designers and manufacturers to work on improving security measures.
According to two surveys carried out by Network World, a mere 7% of firms and manufacturers have a well-defined IoT strategy, and more than 50% are concerned about security risks associated with their devices.
BDO advisory firm’s research indicates that more than a quarter of manufacturers lack a security policy for their vendors or IoT partners.
Google search traffic shows a 265% increase in cybersecurity technology trends since the start of the COVID-19 global pandemic.
2. Targeted Ransomware Attacks in Cybersecurity
Targeted ransomware refers to a type of malware that seizes a victim’s data and demands payment in return for its release, with the payment usually requested in cryptocurrency.
As per a report issued by the US government, there are over 4,000 ransomware attacks recorded on a daily basis.
With its widespread prevalence, targeted ransomware has emerged as the most prominent form of malware to date. According to Cybercrime Magazine, in 2021, a targeted ransomware attack is expected to happen every 11 seconds, not even accounting for attacks on individuals.
The most substantial sum paid out for a single targeted ransomware attack in 2021 was $40 million, and the average ransom demand reached $200,000 in 2020.
Although ransomware attacks can occur globally, they are more prevalent in nations with greater access to internet services.
More than 18% of ransomware attacks happen in the United States, rendering it the country most affected by this form of cyberattack.
Given the fast-evolving nature of targeted ransomware attacks, cybersecurity experts anticipate their prevalence to persist and grow in the forthcoming years.
Around 84% of businesses intend to continue some level of remote work even after the relaxation and lifting of COVID-19 restrictions, heightening the potential for data breaches.
Cybercrime Magazine has projected targeted ransomware damages to surpass $20 billion in 2021, emphasizing the need for enhanced security, particularly for small and medium-sized enterprises.
3. Evolution Of Multi-Factor Authentication in Cybersecurity
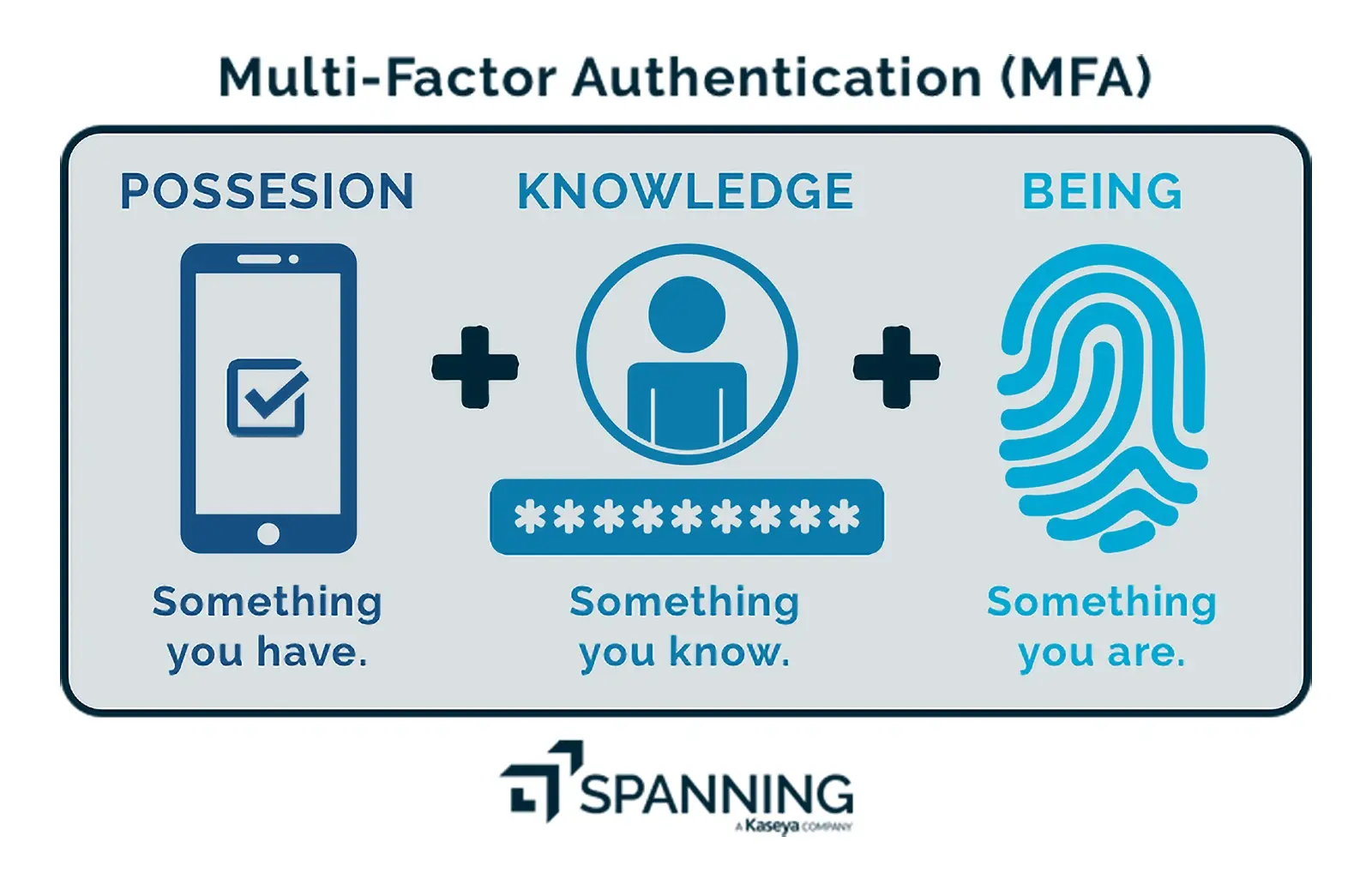
Source: Spanning
Multi-factor authentication refers to an electronic authentication technique that allows users to access a website or application by presenting two or more forms of identity proof to an authentication system.
“Multi-factor authentication” receives 4.4k searches every month, showing a 113% growth trend in the last 5 years.
The multi-factor authentication market was worth more than $10 billion in 2020, as per BusinessWire’s report. The report also anticipates that this figure will exceed $28 billion by 2026.
Although multi-factor authentication is generally deemed to be extremely secure, companies such as Microsoft are advising users to refrain from using SMS and voice authentication methods due to their elevated security vulnerabilities.
Despite the fact that experts recommend using SMS authentication if no other security options are available, it is an unencrypted type of messaging that lacks security. SMS authentication methods are still susceptible to automated “man in the middle” attacks.
The multi-factor authentication methods used in online banking, which are primarily conducted through SMS verification, are at high risk of being inefficient. To decrease the likelihood of unauthorized access to accounts, cybersecurity professionals are increasingly advocating for hardware security keys to be used for verification whenever feasible.
4. Increased Attacks On Cloud-Based Services
At the forefront of cybersecurity risks are cloud-based services.
While Google search traffic only shows a 151% trend increase, the rapid adoption of remote work pushes companies to rely more on these cloud-based technologies to communicate and collaborate.
Misconfigured cloud settings pose a significant cybersecurity risk, leading to costly issues such as data breaches, unauthorized network access, insecure interfaces, and account takeovers.
Ensuring effective management and minimizing potential cloud-based security threats is critical for companies, as the average cost of a data breach according to Security Today is over $3.5 million. The US and Canada are the most targeted countries, with losses totaling $7.91 million and $4.74 million, respectively. A recent cloud security report found that 68% of companies consider the misconfiguration of assets to be one of the most significant contributors to cloud-based security risks.
In addition, 75% of companies are either concerned or very concerned about their cloud security and the threats that exist. According to a report by Veronis, cloud-based cyberattacks rose by nearly 630% between January and April last year, and it is estimated that 20% of organizations’ data breaches were caused by remote workers using company cloud-based platforms. These factors lead us to the next trend in cybersecurity.
5. New Tools To Combat Remote Work Vulnerability
As the COVID-19 pandemic continues to evolve globally, a growing number of companies are opting to offer work-from-home options for their employees. Prior to the pandemic, telecommuting was only available to about 7% of private business employees.
Source: Pew Research Center
Upwork’s report states that by the end of 2025, over 35 million Americans will be working remotely, indicating an 87% increase compared to pre-pandemic statistics. As more employees use home networks and devices connected to corporate platforms, cybercriminals are increasingly breaching critical corporate systems and services.
In fact, HP reports a 238% rise in global cyberattacks since the pandemic began. To manage operations and reduce risk, organizations can adopt Identity and Access Management Tools (IAM). IAM solutions analyze user activity, simplify secure sign-in procedures based on corporate connective habits, and prompt users for additional authentication when necessary.
6. Organizations Invest In Real-Time Data Monitoring
Real-time data monitoring involves continuously updating data streams used to protect an organization’s IT environment, typically cloud-based technology. By monitoring data in real time, IT and security professionals can quickly respond to data breaches, minimizing the risk of financial loss.
Additionally, organizations can track and document data over extended periods, identifying anomalies in system and application behavior as they arise, also known as “trend monitoring.” According to a Deloitte review, third-party software is responsible for detecting up to 70% of all data breaches rather than an organization’s security team. Analyst firm IDC predicts that the cybersecurity software market will increase spending by almost 9% annually and is expected to exceed $133 billion by 2022. They also estimate that enterprises spend over $21 billion annually on security service providers to ensure continuous data monitoring, thereby reducing and preventing cyberattacks.
7. More Social Engineering Attacks in Cybersecurity
Social Engineering Attacks refer to a range of deceptive tactics employed by cybercriminals to manipulate users into revealing sensitive information, which can result in financial loss and other security risks.
Searches for “social engineering attack” have increased by 316% in 5 years.
Social engineering attacks pose a threat as they exploit human weaknesses and errors rather than technical vulnerabilities. This makes them less predictable than other types of cyberattacks, and perpetrators can gain access to sensitive information and financial assets. Social engineering attacks take various forms and can happen in any situation where human interactions occur.
These are the top five social engineering attacks:
- Baiting
- Quid Pro Quo
- Phishing
- Pretexting
- Tailgating
Baiting
One of the most prevalent forms of baiting is the distribution of malware through physical mediums. Attackers may leave items such as flash drives infected with malware in places where they are likely to be found by victims. When the victim plugs the flash drive into a device, the malware is then installed on the system.
Quid Pro Quo
Similar to baiting, quid pro quo social engineering attacks involve a hacker offering compensation or service in exchange for data or login information. Usually, the perpetrator poses as a tech expert calls the victim, and offers to upgrade their system in exchange for login credentials.
Phishing
Phishing is a social engineering attack that uses an automated platform to send digital messages that aim to create a sense of urgency, prompting users to disclose sensitive information. It is considered the most prevalent form of social engineering attack, with 22% of all data breaches involving phishing, according to Verizon.
Pretexting
Pretexting is a type of social engineering attack that involves a perpetrator presenting a false pretense to manipulate a victim into giving away sensitive information. It is frequently the initial stage in a more elaborate scheme to gain access to the victim’s data.
Tailgating
The act of tailgating is a social engineering tactic used to deceive employees into granting physical access to a company’s premises. Once the perpetrator gains entry into the restricted area, they use electronic devices and software to breach the network and extract valuable data.
8. Increased Demand For Cybersecurity Professionals
The need for cybersecurity professionals is a common thread across all the previously discussed topics, and this demand is well-founded.
According to Google search data, the market for cybersecurity jobs has seen an increase of 9,500% over 10 years.
According to the Bureau of Labor Statistics, the cybersecurity sector is expected to experience a growth of over 30% in the next ten years, making it the fastest-growing industry in the United States. Additionally, some projections indicate that there would be more than 3.5 million unfilled positions in the global cybersecurity workforce by the end of 2021.

Source: Cybersecurity Ventures
A report published by the Harvard Business Review reveals that business owners and organizations worldwide recognize the imminent threat of inadequate cybersecurity. The report highlights that most Chief Security Officers are concerned about the cybersecurity skills gap, and nearly 60% of those interviewed anticipate that the problem will worsen before it improves. The high demand for skilled cybersecurity professionals translates into a high earning potential, with Information Security Analysts earning an average of just over $100,000 per year.
Cybersecurity engineers, on the other hand, earn much more, with salaries ranging from $120,000 to $200,000 per year. Given that global cybersecurity losses were projected to exceed $6 trillion at the end of 2021, it is not surprising that this field is increasingly lucrative for those who remain current and proficient.
Conclusion
The field of cybersecurity is constantly evolving, and there are some important developments to keep an eye on in 2023. With the increasing use of AI and machine learning in cybersecurity, organizations can now detect and respond to threats faster and more efficiently than ever before. However, cybercriminals are also becoming more sophisticated, and social engineering attacks are becoming more common. It is important for individuals and organizations to stay up-to-date on the latest cybersecurity trends and best practices to protect their sensitive information and prevent data breaches. As the demand for cybersecurity professionals continues to grow, there is a great opportunity for those with the right skills and expertise to pursue a lucrative and rewarding career in this field.
Here at CourseMonster, we know how hard it may be to find the right time and funds for training. We provide effective training programs that enable you to select the training option that best meets the demands of your company.
For more information, please get in touch with one of our course advisers today or contact us at training@coursemonster.com




Comments ()